Historical & Current Events dictionary
silk road
or Silk Road
What does silk road mean?
The silk road was a network of historical trade routes across Eurasia, connecting east Asia with the Mediterranean Sea. It was in use in various forms roughly between the second century b.c. to the 15th century a.d.
The Silk Road is also the name of an internet black market that was shut down by the FBI in 2013.
Where does silk road come from?
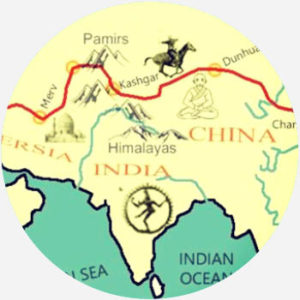
Despite its name, the silk road was not a road. Rather, it was made up of unmarked paths that formed a series of common routes. Nor did it only trade in silk; horses, spices, paper, glass, and other good were carried along the network. The term itself was coined in 1877 by German traveler and polymath Baron Ferdinand von Richthofen, translated into English as the silk road or route by the 1890s. Traders or inhabitants along the silk road, according to Valerie Hansen’s history of it, referred to the trading network as the road leading to whatever next major city lay ahead, among other names.
Richthofen’s concept of the silk road described the specific link between China and Rome across which silk was transported. But the current conception of the silk road is much broader. Maps of the silk road chart land and maritime paths that stretch from Japan to Venice, crossing India, Tibet, Iran, the Arabian Peninsula, Turkey, and Egypt.
The earliest incarnations of the silk road connected China with central Asia, when the Han dynasty opened trade between 200 and 100 b.c. In the first century b.c., this trade reached Rome. Trade throughout Eurasia continued through the Middle Ages. Routes changed at times, products evolved, and dynasties shifted. Nevertheless, trade between the East and the West continued, with the silk road playing a major role not just in economic transactions between and among Eastern and Western cultures, but also in linguistic, political, religious, cultural, and intellectual exchange. New methods and technologies, particularly new sea routes, gradually supplanted the silk road after the late 15th century.
Though the ancient route is no longer used, a modern iteration may be on the horizon. In 2017, China pledged billions of dollars for the “One Belt One Road” project meant to act as a “new silk road.” The project, whose original vision reaches back to 2013, is intended to economically connect parts of eastern Europe, North Africa, the Middle East, and other regions that have pledged their participation. Most of the project will consist of building infrastructure to facilitate trade.
The Silk Road is also the name of an internet black market that allowed users to find drugs, hitmen, forgers, hackers, and counterfeiting services such as fake passports and IDs. It was accessed via the computer network Tor, and customers used the virtual currency bitcoin to make their purchases. In 2013, the FBI brought the network and its creator Ross Ulbricht down, seizing its servers. Ulbricht was sentenced to life in prison without parole.
Examples of silk road
Note
This is not meant to be a formal definition of silk road like most terms we define on Dictionary.com, but is rather an informal word summary that hopefully touches upon the key aspects of the meaning and usage of silk road that will help our users expand their word mastery.